Knee Joint Surgery: Everything You Need to Know
Knee joint surgery, particularly total knee arthroplasty (TKA), is an important treatment option for improving pain and functional impairment caused by knee joint diseases. This article will provide a detailed overview of the current state of knee joint surgery, its principles, suitable candidates, preoperative preparations, postoperative effects, case analysis, developmental trends, and conclusions to help readers gain a comprehensive understanding of this procedure.
I. Current State of Knee Joint Surgery in the United States
In the United States, the demand for knee joint surgery has been steadily increasing. According to statistics, approximately 700,000 total knee arthroplasties are performed each year, primarily targeting severe knee joint damage due to osteoarthritis, trauma, and other conditions. With an aging population and an increase in sports injuries, more individuals are opting for surgery to restore knee function. Recent advancements in minimally invasive techniques and robotic-assisted technologies have made surgeries safer and recovery faster.
II. Principles of Knee Joint Surgery
The fundamental principle of knee joint surgery is to remove damaged cartilage and bone and replace them with artificial implants to restore normal joint function. In total knee arthroplasty, the surgeon removes the damaged portions of the femur and tibia and replaces them with prosthetic components made of metal and plastic. This procedure aims to eliminate friction between bones, thereby reducing pain and improving the range of motion.
III. Suitable Candidates for Knee Joint Surgery
Candidates for knee joint surgery typically include:
•Patients with Severe Knee Pain: Those who have not found relief from non-surgical treatments (such as physical therapy or medication).
•Patients with Functional Impairment: Individuals whose daily activities are significantly limited, such as walking or climbing stairs.
•Imaging Results: Patients with X-ray or MRI findings indicating significant joint damage or degeneration.
IV. Preoperative Preparations for Knee Joint Surgery
Before undergoing knee joint surgery, patients need a comprehensive evaluation that includes:
•Physical Examination: To ensure there are no other health issues that could affect the surgery.
•Imaging Studies: Such as X-rays or MRIs to confirm the extent of damage.
•Medication Management: Certain medications (like non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) may need to be stopped before surgery to reduce bleeding risks.
•Home Environment Preparation: Ensuring that the home is conducive to recovery, such as having clear pathways and necessary assistive devices.
Specific Preparation Steps:
1.Maintain Good Oral Health: Complete any dental work at least six weeks before surgery to prevent infections.
2.Quit Smoking: Aim to stop smoking at least 30 days before and two months after surgery to reduce complication risks.
3.Healthy Diet and Exercise: Follow a balanced diet, maintain a healthy weight, and engage in moderate exercise as recommended by your doctor.
V. Postoperative Effects of Knee Joint Surgery
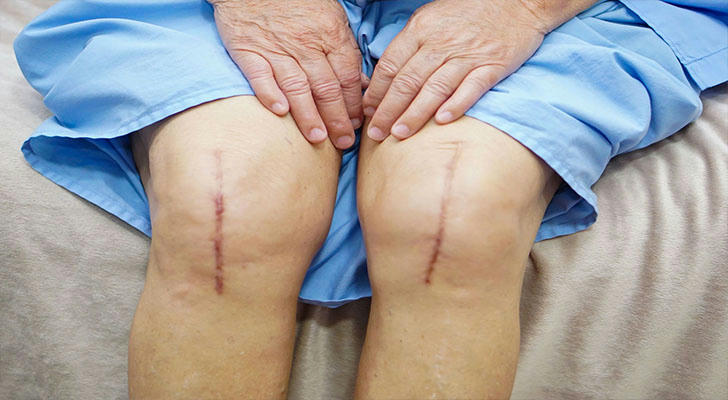
Most patients experience significant pain relief and gradual improvement in mobility during the recovery period. Approximately 90% of patients can return to near-normal living conditions after surgery, enjoying a higher quality of life. Recovery times vary by individual but generally range from six weeks to three months.
Expected Outcomes:
•Improved ability to perform daily activities such as walking and climbing stairs.
•Reduced or eliminated pain, leading to enhanced quality of life.
VI. Case Analysis
Consider a 65-year-old female patient who opted for total knee arthroplasty due to severe osteoarthritis. After surgery, she followed a rehabilitation program guided by a physical therapist. By six weeks post-surgery, she was able to walk independently and resume daily activities like shopping and walking. This successful case illustrates the significant impact of knee joint surgery on improving quality of life.
VII. Development of Knee Joint Surgery
In recent years, advancements in medical technology have brought significant changes to knee joint surgery. From traditional open surgeries to minimally invasive techniques and robotic-assisted procedures, these innovations have made surgeries more precise with shorter recovery times. Additionally, new materials and prosthetic designs have improved the durability and functionality of implants.
Future Trends:
•Robotic-assisted surgeries will further enhance precision.
•Personalized medicine will become a new trend, tailoring treatment plans based on individual patient needs.
VIII. Conclusion
Knee joint surgery in the United States offers many patients the opportunity to regain health and improve their quality of life. Through scientific evaluation, proper preparation, and advanced technology, patients can effectively relieve pain and restore mobility. With ongoing advancements in medical technology, future knee joint surgeries will be even safer and more efficient, bringing hope and change to more individuals. For those considering this type of surgery, understanding relevant information and communicating with healthcare professionals is crucial for ensuring success.
